What Is Manual Therapy?
If you’re dealing with pain, stiffness, or limited range of motion, Manual Therapy might be ideal for you. The best way to find out is to book a consultation with one of our experienced therapists.
Ready for a More Comfortable, Active Life?
Unlock the full potential of your body at Revive Rehab Clinic. Schedule your appointment today and say goodbye to persistent pain!
Why Choose Manual Therapy?
Manual therapy is a collection of hands-on techniques that trained healthcare professionals, such as physiotherapists, chiropractors, osteopaths, and massage therapists, use to diagnose, treat, and prevent musculoskeletal conditions and pain. Manual Therapy offers a non-invasive way to relieve chronic and acute pain. It aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, accelerate tissue healing, and restore normal function. Manual therapy involves skilled manipulation and mobilization of joints and soft tissues, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, and fascia.
Boost Your Physical Potential With Our Manual Therapy
Manual therapy can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapeutic approaches, including exercise therapy, electrotherapy, and patient education. It is commonly employed in the management of various musculoskeletal conditions, such as back pain, neck pain, joint stiffness, sports injuries, and postural problems. However, its efficacy may vary depending on the specific condition and individual patient factors. To ensure safety and effectiveness, Manual therapy must be carried out by experienced and qualified physiotherapists in Surrey.
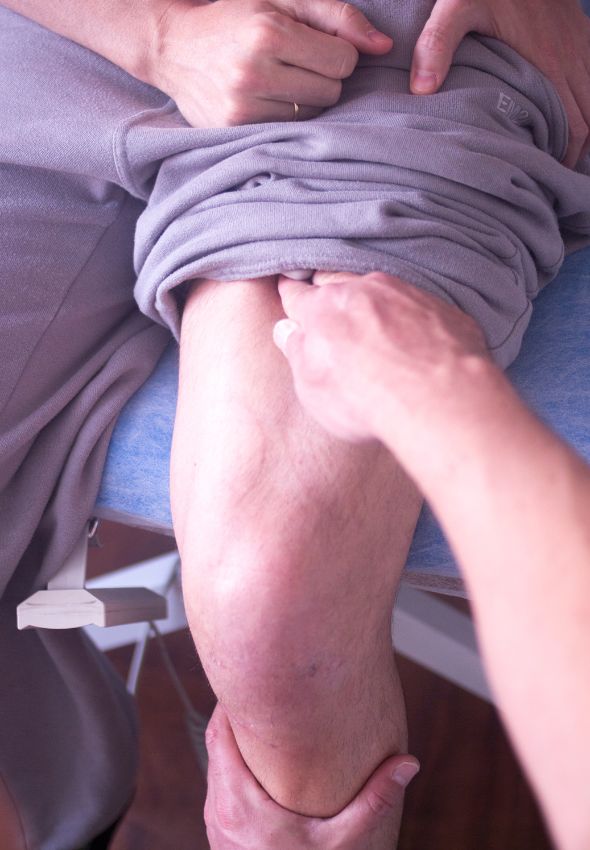
Manual Therapy Techniques
Manual therapy is a group of physical techniques physiotherapists use to treat injuries, pain, and other conditions. Some of the most common manual therapy techniques include:
1. Joint mobilization: This technique involves gently and passively moving a joint to restore and enhance mobility.
2. Joint manipulation: This technique, often associated with chiropractic care, involves applying a high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust to a joint to restore normal movement and function.
3. Soft tissue mobilization: This technique is used in massage techniques by our RMT Surrey team, such as myofascial release and trigger point therapy, to release tension and tightness in muscles and fascia.
4. Stretching: Manual stretching techniques improve flexibility and range of motion in muscles and joints.
5. Muscle energy techniques (MET): A form of stretching that aims to improve muscle function and joint mobility by having the patient actively contract the muscle while the team of our Abbotsford physiotherapists applies resistance.
6. Strain Counterstrain: The physiotherapist positions the patient comfortably, reducing pain and tension in a specific muscle or joint.
7. Manual traction: This technique involves gently pulling or stretching the spine or limbs to relieve pressure on nerves or promote joint decompression.
Types Of Manual Therapy Treatments Explained
Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization is a manual therapy technique healthcare professionals use to enhance joint mobility and function at our Surrey Active Rehab Clinic. It involves applying graded forces to joint surfaces to restore standard movement patterns, reduce pain, and improve joint health.
The physiotherapist conducts a thorough assessment before administering joint mobilization, which helps determine the appropriate techniques and treatment plan. Joint mobilization techniques are applied in specific directions defined by the joint’s anatomy and the desired therapeutic outcome.
Overall, joint mobilization is a versatile and effective treatment approach used in various healthcare settings to address joint dysfunction and improve overall patient movement and function.
Joint Manipulation
Joint manipulation, also known as spinal manipulation, is a manual therapy technique used to address joint dysfunction and related symptoms such as pain and restricted movement. It involves applying a high-velocity, low-amplitude thrust to a specific joint in the spine or extremities to restore proper joint function, alignment, and mobility.
Joint manipulation effectively manages musculoskeletal conditions, including low back pain, neck pain, headaches, and joint dysfunctions. When performed by qualified physiotherapists and in appropriate clinical scenarios, it can provide significant relief and improve function for patients with musculoskeletal complaints.
Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization is a hands-on technique to address musculoskeletal pain, tension, and dysfunction by manipulating the body’s soft tissues. It involves assessing the patient’s musculoskeletal system, positioning them comfortably, and conducting various manual techniques, such as massage, myofascial release, trigger point therapy, deep tissue massage, and friction massage.
The methods are applied in specific directions and intensities to achieve therapeutic goals. Soft tissue mobilization can relieve pain, improve flexibility and range of motion, enhance circulation and tissue healing, reduce muscle spasms and stiffness, and promote relaxation.
After the treatment, self-care strategies may be recommended to maintain the benefits and prevent the recurrence of symptoms.
Stretching
Manual stretching is a fundamental component of physical therapy and fitness programs. It involves the deliberate lengthening of muscles and surrounding tissues to improve flexibility, range of motion, and overall function. Before initiating a stretching program, the manual therapist assesses the patient’s flexibility, joint mobility, and any areas of muscle tightness or restriction.
Manual stretching involves the therapist applying controlled pressure and traction to lengthen specific muscle groups. These techniques include static stretching, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF), assisted stretching, dynamic stretching, and breathing and relaxation techniques.
The manual therapist tailors the stretching program to the patient’s needs and goals. After stretching, the physiotherapist may recommend self-care strategies to optimize the benefits of the stretching session and minimize post-exercise soreness.
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET)
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET) involve active muscle contraction followed by a controlled stretch or mobilization by the physiotherapist. It improves joint mobility, alleviates muscle tightness, corrects musculoskeletal imbalances, and reduces pain.
Before applying MET, the manual therapist thoroughly assesses the patient’s musculoskeletal system to identify areas of muscle weakness, tightness, or joint restrictions. MET techniques involve isometric contraction, hold-relax, reciprocal inhibition, repetition, and progression.
MET can benefit musculoskeletal conditions, but caution should be exercised in certain situations. MET is often integrated into comprehensive treatment plans, including other manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercise, and patient education, to optimize outcomes and address underlying biomechanical issues.
Strain Counterstrain
Strain Counterstrain is a manual therapy approach used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction. It involves identifying and releasing tender points within muscles and connective tissues. The technique is passive, with the physiotherapist positioning the patient’s body in a comfortable and relaxed position that shortens the muscle associated with the tender point.
During the shortening phase, the therapist monitors the patient’s response, looking for signs of tissue relaxation, decreased tenderness, and improved range of motion. Strain Counterstrain can effectively alleviate acute and chronic musculoskeletal pain, including muscle strains, trigger points, joint dysfunction, and postural imbalances.
However, it may not be suitable for all patients, and the physiotherapist should perform a thorough evaluation and consider the patient’s needs and medical history before applying Strain Counterstrain techniques.
Manual Traction
Manual traction is a therapeutic technique used in manual therapy to stretch and decompress the spine or extremities. The manual therapist assesses the patient’s musculoskeletal system to determine traction appropriateness and specific strategies. Our Surrey physiotherapist applies controlled traction or pulling force to the affected body area using their hands during manual traction.
Traction may be applied intermittently or continuously for a specified duration, typically ranging from a few seconds to several minutes. Manual traction should be performed by trained and qualified healthcare professionals who understand the anatomy and biomechanics of the joints and soft tissues, and care should be taken to avoid excessive traction force or duration.
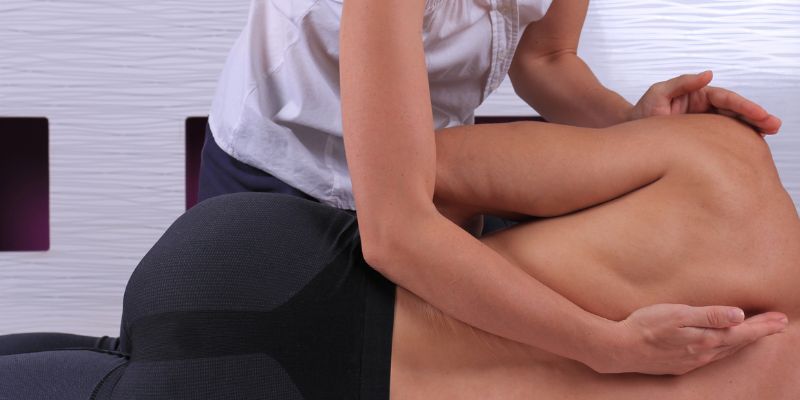

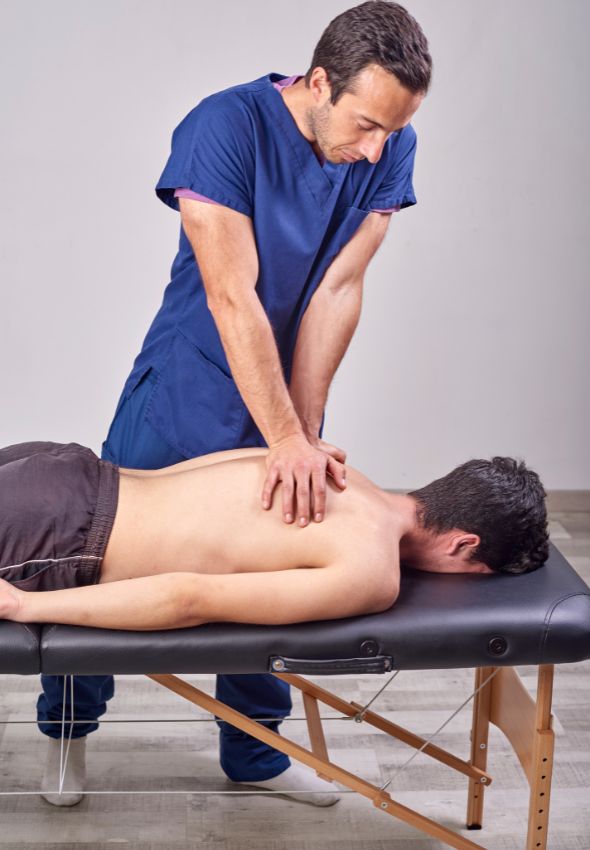
Benefits Of Manual Therapy
Manual therapy is a type of treatment that offers various benefits to people who have musculoskeletal conditions, injuries, or difficulties with movement. Some of the main benefits include:
1. Pain relief: Various manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization, manipulation, soft tissue mobilization, and trigger point therapy, can help reduce musculoskeletal pain by decreasing muscle tension, improving joint mobility, and releasing tight or restricted tissues.
2. Improved range of motion: Manual therapy can enhance flexibility and range of motion in joints by addressing joint restrictions, muscle tightness, and adhesions, allowing for smoother and more efficient movement patterns.
3. Enhanced tissue healing: Manual therapy techniques like soft tissue mobilization and massage can improve circulation and lymphatic drainage, delivering nutrients to injured tissues and removing metabolic waste products, which may facilitate healing.
4. Correction of postural imbalances: Manual therapy interventions can help correct postural deviations and imbalances by improving joint alignment, addressing tight or weakened muscles, and promoting better body awareness and alignment.
5. Reduced muscle tension and spasm: Techniques such as soft tissue mobilization, trigger point therapy, and muscle energy techniques can help reduce muscle tension, spasms, and hypertonicity, promoting relaxation and reducing the risk of muscle strains or overuse injuries.
6. Improved joint stability: Joint mobilization and manipulation techniques can enhance joint proprioception and stability by restoring standard joint mechanics, reducing hypermobility or hypomobility, and improving neuromuscular control around the joint.
7. Prevention of injuries: Regular manual therapy sessions, combined with appropriate exercise and movement strategies, can help prevent injuries by addressing underlying biomechanical dysfunctions, promoting tissue resilience and adaptability, and optimizing joint mobility.
8. Enhanced athletic performance: Athletes often benefit from manual therapy as part of their training regimen, as it can help reduce the risk of injuries, optimize movement efficiency, and improve performance by addressing muscle imbalances, enhancing flexibility, and promoting optimal joint function.
9. Stress reduction and relaxation: Manual therapy techniques such as massage and myofascial release can promote relaxation, reduce stress levels, and induce a sense of well-being by stimulating the release of endorphins and promoting parasympathetic nervous system activity.
10. Improved quality of life: Manual therapy can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life by addressing pain, improving mobility, and enhancing overall musculoskeletal function, allowing them to participate more fully in daily activities, work, recreational pursuits, and social interactions.
It’s important to note that the benefits of manual therapy may vary depending on individual factors such as the nature and severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health status, and their response to treatment. Manual therapy is often most effective when combined with other therapeutic modalities, such as exercise therapy, patient education, ergonomic modifications, and lifestyle interventions.
Who Needs Manual Therapy?
Manual therapy can be helpful for people who experience musculoskeletal pain, dysfunction, or movement limitations. The treatment involves joint mobilization, manipulation, soft tissue mobilization, and trigger point therapy that can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Here are some examples of who may benefit from manual therapy:
Manual therapy can alleviate pain associated with conditions such as
- neck pain
- low back pain
- sciatica
- rotator cuff injuries
- frozen shoulder
- osteoarthritis
- bursitis
- patellofemoral pain syndrome
- meniscus tears
- plantar fasciitis, and
- tendonitis.
Manual therapy techniques can improve joint mobility and flexibility, making them beneficial for individuals with
- Joint stiffness or decreased range of motion (e.g., post-surgical stiffness, adhesive capsulitis)
- Muscle tightness or contractures
- Functional limitations due to musculoskeletal conditions (e.g., difficulty walking, reaching overhead)
Manual therapy can be crucial in injury prevention, performance optimization, and rehabilitation for athletes and active individuals participating in sports and recreational activities.
- Address muscle imbalances and asymmetries
- Enhance joint mobility and stability
- Improve flexibility and muscle function
- Accelerate recovery from training and competition-related injuries
Manual therapy techniques can help correct postural imbalances and alignment issues, which may contribute to
- Chronic neck and back pain
- Headaches
- Shoulder impingement
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Manual therapy can be an essential component of post-operative rehabilitation and recovery for individuals who have undergone orthopedic surgery or experienced traumatic injuries. It can help:
- Reduce pain and inflammation
- Improve joint mobility and scar tissue mobility
- Enhance tissue healing and function
- Restore functional independence and quality of life
Manual therapy techniques can address soft tissue restrictions and joint dysfunctions commonly associated with work-related or repetitive strain injuries, such as:
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Tennis elbow
- Thoracic outlet syndrome
- Rotator cuff injuries
Before undergoing manual therapy, seeking advice from a qualified healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist, chiropractor, or osteopath, is essential. A thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and individualized treatment plan based on the individual’s needs, goals, and medical history are essential for effective treatment.
Manual Therapy Vs. Physical Therapy
“Manual therapy” and “physical therapy” are terms often used interchangeably, but they refer to different rehabilitative care aspects. Here’s a breakdown of each:
Manual Therapy:
Definition: Manual therapy is a broad category of hands-on techniques healthcare professionals use to diagnose, treat, and prevent musculoskeletal conditions. It includes joint mobilization, manipulation, soft tissue mobilization, muscle energy techniques, and strain counterstain.
Focus: Manual therapy addresses specific dysfunctions in joints, muscles, and soft tissues through skilled manipulation and mobilization techniques. It aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, restore standard movement patterns, and enhance overall musculoskeletal function.
Practitioners: Manual therapy techniques are typically performed by healthcare professionals such as chiropractors, osteopaths, physical therapists, massage therapists, and athletic trainers who have received specialized training in manual therapy techniques.
Application: Manual therapy techniques are often integrated into comprehensive treatment plans for musculoskeletal conditions, either as standalone interventions or in combination with other therapeutic modalities such as exercise therapy, patient education, and modalities like heat or ice therapy.
Physical Therapy:
Definition: Physical therapy (PT), or physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession focused on helping individuals recover from injury, post-surgery rehabilitation, or illness and improve their overall physical function and mobility. It encompasses various interventions to restore movement, reduce pain, and promote functional independence.
Focus: Physical therapy addresses a broad spectrum of musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiopulmonary, and other health conditions through various interventions such as exercise therapy, manual therapy, patient education, therapeutic modalities (e.g., ultrasound, electrical stimulation), and functional training.
Practitioners: Physical therapists are licensed healthcare professionals who evaluate, diagnose, and treat individuals with movement-related disorders. They design customized treatment plans based on the patient’s specific needs and goals, utilizing a combination of evidence-based interventions to optimize outcomes.
Application: Physical therapy services are provided in various settings, including hospitals, outpatient clinics, rehabilitation centers, and home health settings. Treatment may involve manual therapy, therapeutic exercise, modalities, education, and functional training to address the individual’s impairments and functional limitations.
In summary, while manual therapy is a specific subset of techniques used within the broader scope of physical therapy, physical therapy encompasses a wide range of interventions to promote physical health, function, and well-being across diverse patient populations and conditions. Physical therapists often utilize manual therapy techniques as part of a comprehensive treatment approach to address musculoskeletal issues and optimize patient outcomes.
